For instance, a relative risk of 70% corresponds to an odds ratio of 07/(107)=233 however, it is clearer to say to the layman that a certain risk factor "increases the probability of a disease by 70%" (relative risk) rather than that it "increases the probability of the disease by an odds ratioThe relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative riskFeb 07, 14 · It has been proposed that the sample odds ratio is a good estimate of the population relative risk and can be interpreted as a relative risk when the disease or outcome is rare in the population, typically when the prevalence is less than 10%

Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
Should i use odds ratio or relative risk
Should i use odds ratio or relative risk-May 04, 09 · When the outcome risk is 01 or less, odds ratios and risk ratios agree well for risk ratio values ranging from 01 to 10 in all 3 figures When cumulative incidence is 10, the odds ratio is within 10% of the risk ratio for risk ratios ranging from 01 to 18 in Figure 1, from 055 to 10 in Figure 2, and from 04 to 25 in Figure 3 WhenThis is not true for relative risk Switching the rows or columns inverts the odds ratio For example, the odds ratio for no cough given a history of bronchitis = (247/26)/(1002/44) = 0417 = 1/2397 This is the reciprocal of the OR for cough There are only two possible odds ratios, as switching both rows and columns gives


Case Control Study Vs Cohort Study Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo
Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) Relative Risk = Probability / Probability Odds Ratio = Odds / Odds Now that you have a general idea of what odds ratio and relative risk are you need to know when to useSep 16, 02 · While some suggest using only relative risk 3, or absolute risk reduction 4, others advocate use of the number needed to treat criteria 5, 6, and some consider the odds ratio to be the method of choice 2 Obviously, the choice of methodThe odds ratio supports clinical decisions by providing information on the odds of a particular outcome relative to the odds of another outcome In the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocol
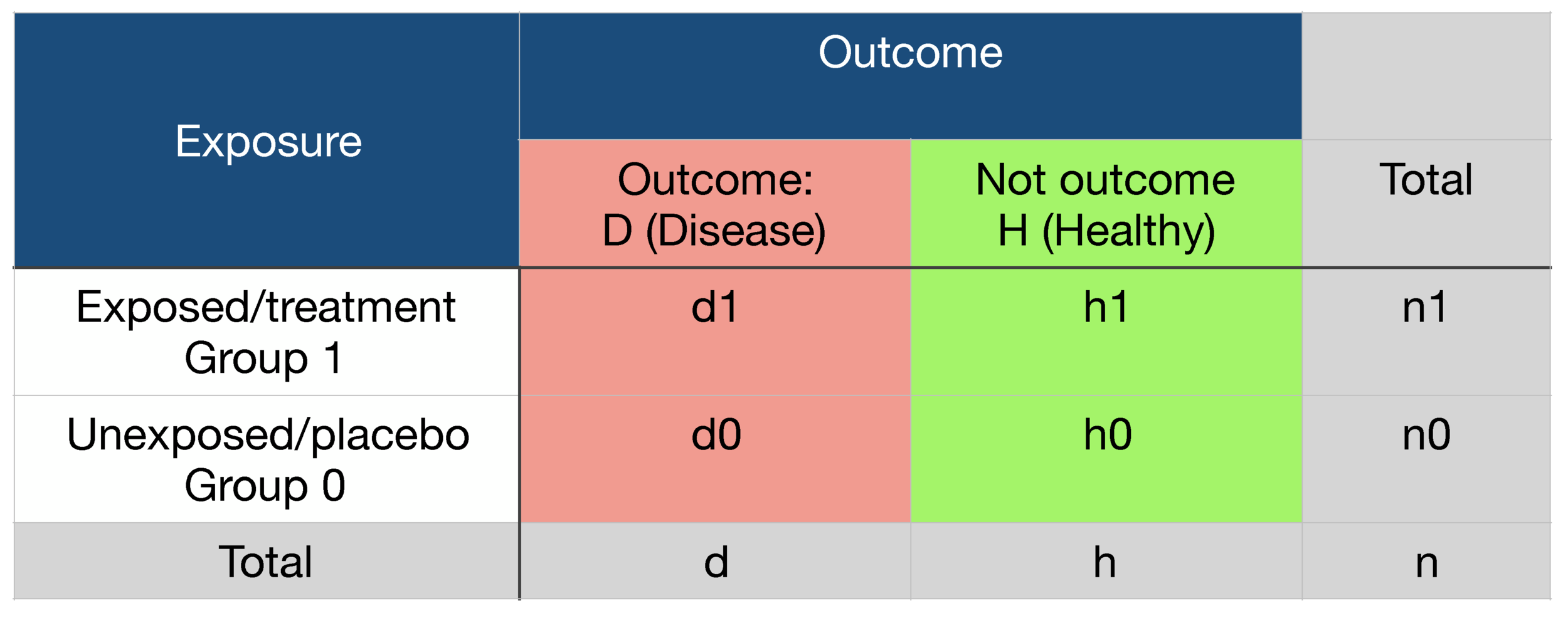
Dec 30, 16 · INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculatedIt is assumed that, if the prevalence of the disease is low, then the odds ratio approaches the relative risk Case control studies are relatively inexpensive and less timeconsuming than cohort studies In this case the odds ratio (OR) is equal to 16 and the relative risk (RR) is equal to 865 What does a risk ratio of 075 mean?Or population of interest The relative risk (RR) is the risk of the event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is
Pute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greaterMay 15, 14 · The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio May 15, 14 • ericminikel The other day I was emailing with a statistical genetics colleague about a rare SNP associated with a phenotype I stated that the minor allele frequency (MAF) was 07% in cases and 01% in controls, for a risk ratio of 7 After clicking send, I felt a twinge of regretAug 07, 14 · If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a



When To Use Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
The odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies1 we can calculate relative risk IF we can estimate probabilities of an outcome in EACH group 2 we can't do that in case control studies 3 we can calculate the odds ratio even if we don't know the probabilities in the groups It would then be nice, if odds ratio was close to relative riskOdds ratio is always larger than Relative Risk, sometimes a lot larger 2 Odds ratios are only useful in true case control studies, which are done because the true incidence of the disease is



Literature Search



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
Jun 01, 12 · For odds ratio the value is calculated by dividing the probability of success by the probability of failure Hence taking a variable X as probability of success and equating it with will give you a sucess ratio of 049 or an odds of 972 to 100 for the sucess of the event I hope this provides an adequate understandingOdds ratio and relative riskAbstract Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



Measures Of Association Ppt Download
Odds ratio Alternatively, the association between vaccination and risk of infection can be summarized using an odds ratio The odds of becoming infected can be estimated as the probability of being infected divided by the probability of not being infected Using the summary table above, theRR and OR are commonly used measures of association in observational studies In this video I will discuss how to interpret them and how to apply them to patJan 08, 16 · You may have noticed that the odds ratio and relative risk are very similar in this case This happens when the proportions being compared are both close to 0 Which one you decide to use is a matter of personal preference and perhaps your audience



Relative Risk And Odds Ratios Examples Calculating Atrium



First Aid Epidemiology Biostatistics Flashcards Quizlet
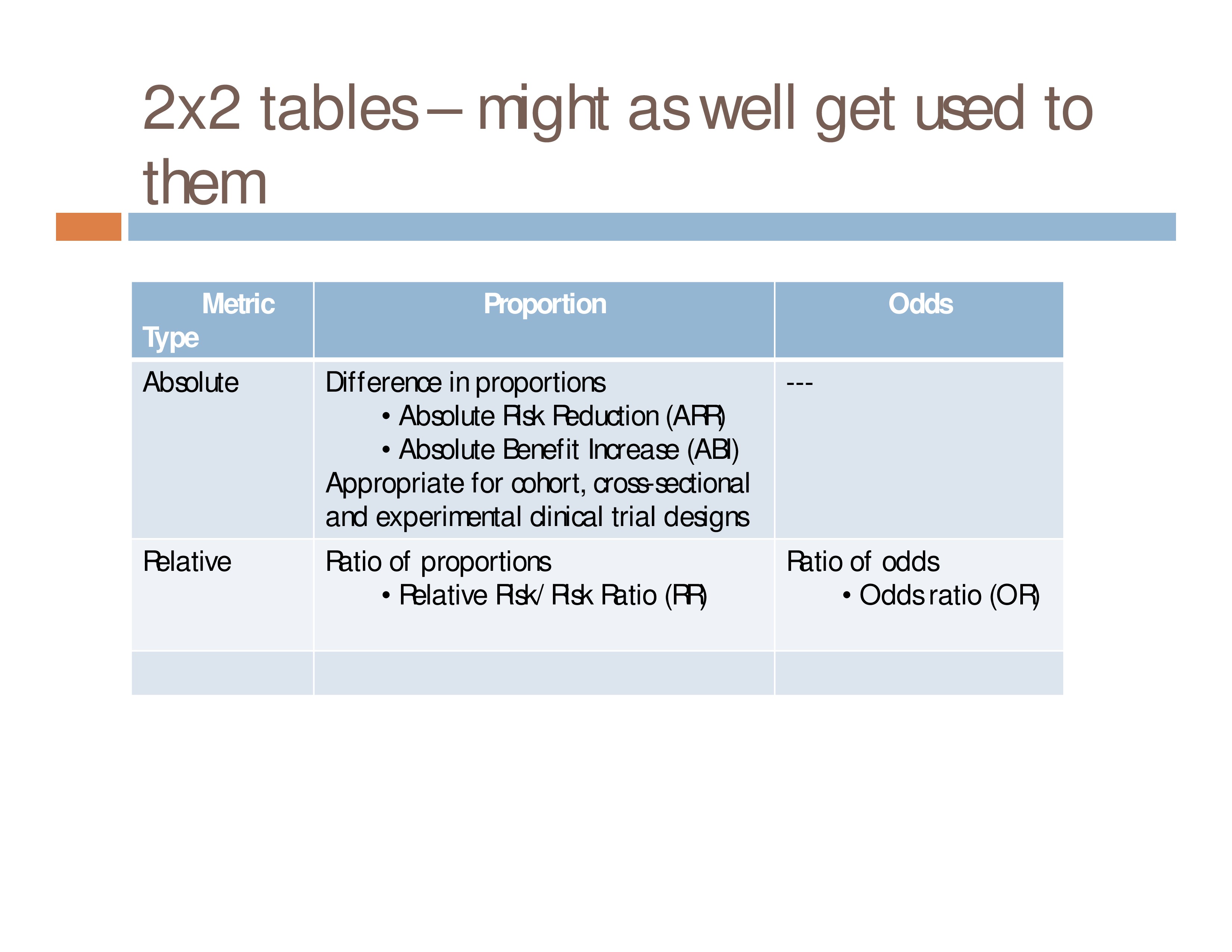
Sep 02, · The Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard)Jun 01, 00 · ODDS RATIOS and relative risks are commonly used to express results in clinical studies The results of cohort studies and casecontrol studies are best expressed as relative risks and odds ratios, respectively The use and interpretation of these ratios are the subject ofOct 01, 07 · Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds) The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (ie the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed)



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



Estimating Risk
Feb 15, 12 · The use of an adjusted odds ratio to estimate an adjusted relative risk or prevalence ratio is appropriate for studies of rare outcome but may be misleading when the outcome is common Such overestimation may inappropriately affect clinical decisionmaking or policy development For example, overestimation of the importance of a risk factorAug 26, · Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three common, but often misused, statistical measures in clinical research In this paper, the authors dissect what each of these terms define, and provide examples from the medical literature to illustrate each of these statistical measures Finally, the correct and incorrect methods to use these measures are summarizedMar 28, 1998 · Even with initial risks as high as 50% and very large reductions in this risk (odds ratios of about 01), the odds ratio is only 50% smaller than the relative risk (01 for the odds ratio compared with a true value for the relative risk of 02)



Average Values Measures Of Association N Absolute Risk The Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Provide A Measure Of Risk Compared With A Standard N Attributable Ppt Download


Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be
The baseline risk is the denominator of relative risk, ie, the risk of the group being compared to In our example, this would be the risk of heart attack for the normal range If this baseline risk is high, then a relative risk of 5 would be alarming;May 18, 12 · A risk ratio of 10 indicates identical risk among the two groups A risk ratio greater than 10 indicates an increased risk for the group in the numerator, usually the exposed group A risk ratio less than 10 indicates a decreased risk for the exposed group, indicating that perhaps exposure actually protects against disease occurrenceIf the baseline risk is small, then a relative risk of 5 may not be too serious



Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table



Relative Risks Odds Ratios John Snow S Cholera Investigations
Sep 01, 02 · While some suggest using only relative risk 3, or absolute risk reduction 4, others advocate use of the number needed to treat criteria 5,6, and some consider the odds ratio to be the method of choice 2Jan 10, 13 · Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect sizeThe basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (the relative risk is also called the risk ratio) The odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event in the Treatment group to the odds of an event in the control group



Measuring Of Risk



1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table
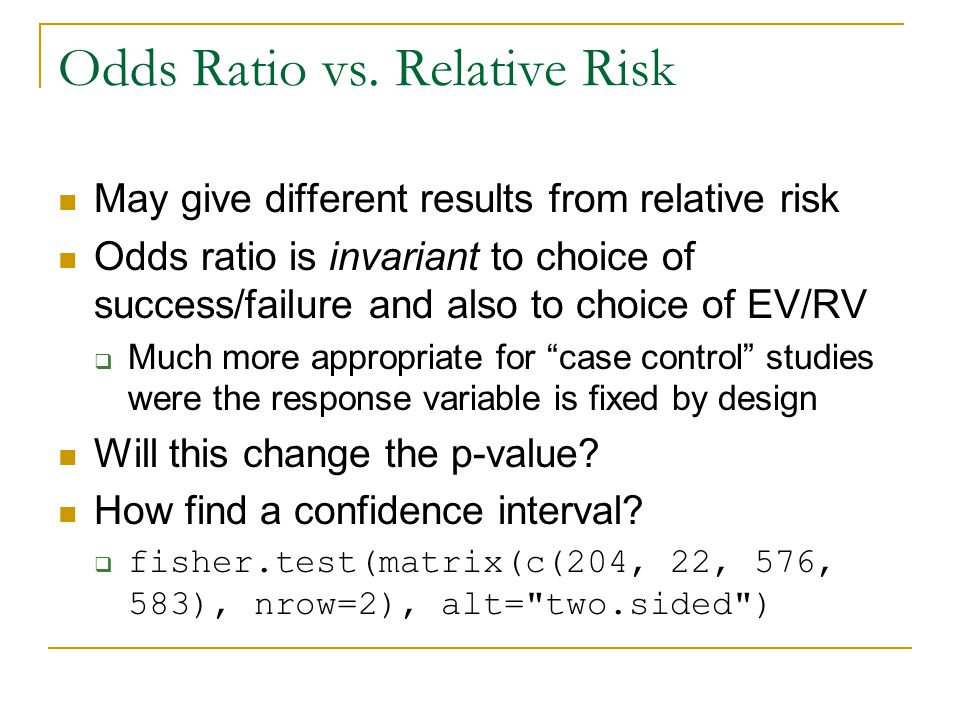
Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratio2) Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the nonobese Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter9222 Measures of relative effect the risk ratio and odds ratio Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a)For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy On Vimeo



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated
Feb 17, 21 · For example, a relative risk of 15 would suggest a 50% increase in risk, whereas a relative risk of 05 would suggest a 50% decrease in risk Odds ratios The main difference between this and the other two measures is that there is no way of including a2 days ago · Math formula to reproduce a plot comparing Relative Risk to Odds Ratios 3 Relative risk not making sense for metaanalysis 0 odds ratio to relative risk equation, how is it derived?Apr 06, 10 · Therefore Relative Risk = the ratio (A/AC)/(B/BD) To understand Odds Ratio now, lets go through another but similar example A group of 60 individuals with cancer are being evaluated to see they were exposed to a particular toxin X



Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals
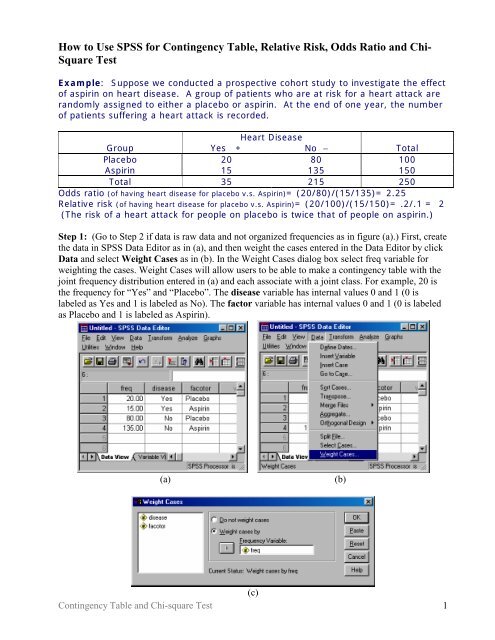
Hot Network Questions Did AlphaZero also have to learn that each piece has a value?Aug 01, 05 · In our example, the odds ratio of treatment to control group would be 35 (15 divided by 043) Risk and relative risk Risk, as opposed to odds, is calculated as the number of patients in the group who achieve the stated end point divided by the total number of patients in the group Risk ratio or relative risk is a ratio of two "risks"Transcribed image text Exercise on Calculation of Relative Risk (RR), Odds Ratio (OR) and NNT (Target 25min) Women with a genetic condition are at risk of jaundice during late pregnancy A drug is available that may reduce this risk A parallel groups study compares rates of jaundice with active and placebo treatment during pregnancy


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Relative Risk Http Www Slideshare Net Terryshaneyfelt7 What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean Study Skills Research Methods Study Tips
The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed groupThe more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 If the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative risk vs Odds ratio



Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk



Math3010 Week 6



Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Incidence Download Scientific Diagram



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Glossary Of Research Terminology



Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056



Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training


Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download


Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People



Reporting The Results Sage Research Methods



Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download



Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice



Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1 How To Memorize Things Math Lessons Public Health Jobs



Odds Ratio Relative Risk



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey



Figure 2 X 2 Table With Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor


Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia



Pdf Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk For Cross Sectional Data Semantic Scholar



Chapter 10 Chi Square Test Relative Risk Odds Ratios



Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube


9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Odds Ratios Are Calculated From Case Control Studies Which Are Described On Slide 14 Odds Ratios Are Only Estimates Of Relative Risks Since True Incidence Rates Cannot Be


How To Use Spss For Contingency Table Relative Risk Odds Ratio



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08



Odds Ratio Wikipedia


Event Based Measures Of Effect Size Asha Journals Academy



Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio



Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram



Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh



Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect



Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To



Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology


Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gp Raj


Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream



Odds Ratio Http Www Slideshare Net Terryshaneyfelt7 What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean Research Methods Academic Research Statistics Math



Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



Wasp Write A Scientific Paper Using Excel 12 Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Sciencedirect



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases



Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj


Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream


Case Control Study Vs Cohort Study Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Updated 13
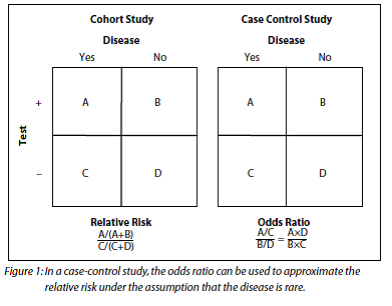


How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy


Epidemiology Stepwards



Answered 32 Chapter 3 Quantifying The Extent Of Bartleby



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International
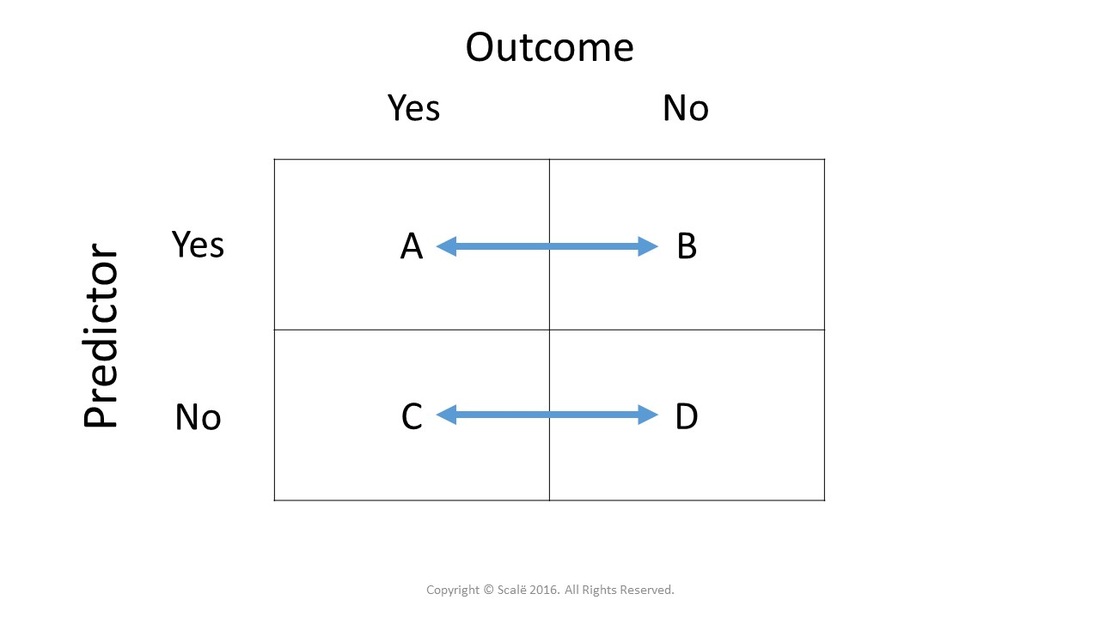


Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Relative Risk Wikipedia



On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Incidence And Prevalence Are Formally Defined On Slide 7 Birth And Death Rates Are Also Estimates Of Absolute Risk Risk Factors Are Identified By Determining


Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data



Related Image Cross Sectional Study Hazard Ratio Odds



Evidence Of Safety Pooled Relative Risk Rr Or Odds Ratio Or And Download Table



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Abdullah Kharbosh What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean By Ebmteacher Casecontrol Cohort T Co Shfiaepl57 عبر Slideshare



Understanding The Odds Ratio And The Relative Risk Simon 01 Journal Of Andrology Wiley Online Library



Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿